|
Race/Ethnicity. The military attracts and retains higher proportions of Blacks and "Other" minority
groups but lower proportions of Hispanics than are in the civilian labor force. As Table 3.3 indicates, the overall proportion of enlisted minorities was higher than in the civilian labor force in FY 1997 (35 and
29 percent, respectively). While Hispanics were underrepresented among enlisted members (8 percent versus 12 percent), the Services have made gains since 1987, when only 4 percent of the enlisted force was
Hispanic.
Table 3.3. FY 1997 Race/Ethnicity of Active Component Enlisted Members,
by Service, and Civilian Labor Force 18-44 Years Old (Percent) |
Race/
Ethnicity |
Army |
Navy |
Marine
Corps |
Air
Force |
DoD |
18-44 Year-Old
Civilians |
White |
56.8 |
64.7 |
67.4 |
73.9 |
64.7 |
71.4 |
Black |
29.7 |
19.5 |
16.8 |
17.4 |
22.1 |
12.3 |
Hispanic |
7.0 |
8.5 |
11.6 |
4.8 |
7.5 |
11.9 |
Other |
6.5 |
7.2 |
4.3 |
3.9 |
5.8 |
4.5 |
Total
|
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
Columns may not add to total due to rounding.
Also see Appendix Table B-25 (Race/Ethnicity by Service and Gender).
Source: Civilian data from Bureau of Labor Statistics Current Population Survey File, September 1997. |
Twenty-two percent of the enlisted force was Black, compared with 12 percent of the
civilian labor force (18-44 year-olds). This near 2:1 ratio for Black members was higher than for FY 1997 accessions, primarily because retention was higher among Blacks than
Whites. The Army had the highest proportion of Black enlisted members in FY 1997 (30 percent).Changes over time in the percentage of Black enlisted members in each Service are shown
in Figure 3.3. Black soldiers in the Army increased from 18 percent in FY 1973 to a high of 33 percent in FY 1981. That proportion decreased to 30 percent by the mid-1980s, in
large part due to an increase in entrance standards and the Army's decision not to renew enlistment contracts of low-scoring members who entered during the ASVAB misnorming.
The proportion of Blacks in the Army has remained stable since 1993 at 30 percent.
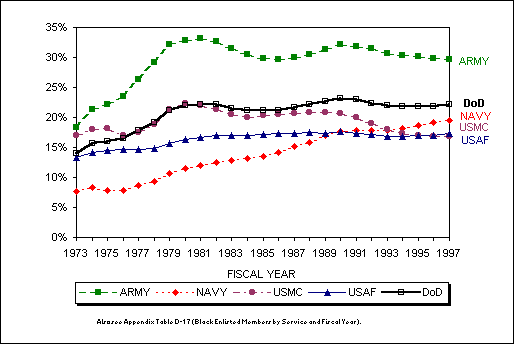 |
Figure 3.3. Blacks as a percentage of Active Component enlisted members, by Service, FYs 1973-1997. The Marine Corps has experienced slight decreases in Blacks during recent years,
paralleling the drop in minority accessions in 1991 and the concomitant decrease in the propensity to enlist among Black youth. Black male propensity declined 15 percentage points between 1991 and 1997. (2) The Navy, on the other hand, exhibited a consistent
long-term increase in the proportion of Blacks, from 8 percent in FY 1973 to 20 percent in FY 1997. In all Services, the percentage of female members who are Black significantly
exceeds the percentage of male members who are Black (Appendix Table B-25)
.In FY 1997, active duty Hispanic enlisted members were a smaller part of the enlisted force than of the civilian labor force in the 18-44 age group (8 percent and 12 percent,
respectively). The highest representation of Hispanics was in the Marine Corps (12 percent). The proportions of "Other" minority individuals in the Army and Navy were
similar (7 percent), while the Air Force and Marine Corps had somewhat less (4 percent). Go to Gender
- Memorandum from F. M. Rush, Acting Assistant Secretary of Defense (Force Management Policy), Subject: 1997 Youth Attitude Tracking Study, January 15, 1998.
go back
|

